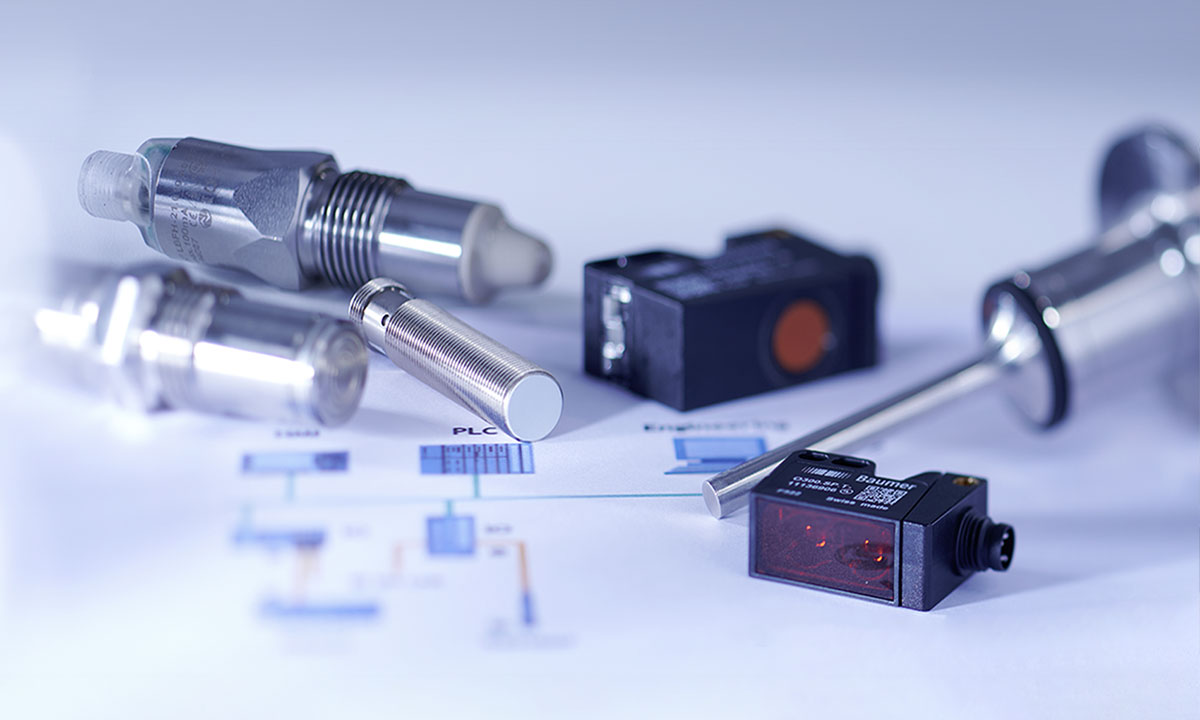
In the realm of modern industry, data is king, and sensors are the unsung heroes that capture this invaluable resource. From monitoring equipment performance to ensuring product quality, industrial sensors play a pivotal role in driving efficiency, precision, and safety across diverse sectors. In this article, we delve into the world of electric and electronic industrial sensors, exploring their significance and the transformative impact they have on industrial operations.
Understanding Industrial Sensors
Industrial sensors are devices designed to detect, measure, and transmit various types of physical parameters within industrial environments. These parameters may include temperature, pressure, humidity, motion, proximity, level, flow, and more. Sensors come in a variety of types, ranging from simple electromechanical switches to sophisticated electronic devices equipped with microprocessors and wireless connectivity.
Key Functions and Features
- Data Acquisition: Industrial sensors serve as the frontline data collectors, capturing real-time information about the operating conditions of machinery, equipment, and processes. This data is then used for monitoring, analysis, and control purposes, enabling proactive maintenance, process optimization, and decision-making.
- Monitoring and Control: Sensors play a crucial role in monitoring critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration to ensure equipment operates within safe and optimal ranges. Additionally, sensors enable closed-loop control systems, where feedback signals are used to adjust process variables and maintain desired performance levels.
- Quality Assurance: In manufacturing and production environments, sensors are utilized to monitor product quality and consistency. By detecting deviations from predefined specifications, sensors help identify defects, prevent costly rework, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards and customer requirements.
- Safety and Environmental Monitoring: Industrial sensors are essential for ensuring workplace safety and environmental compliance. Gas sensors detect hazardous gases, smoke detectors alert to potential fires, and environmental sensors monitor air quality, temperature, and humidity to create a safe and comfortable working environment.
Types of Industrial Sensors
- Temperature Sensors: Thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), and thermistors are commonly used to measure temperature in industrial processes, allowing for precise control and monitoring of heating and cooling systems.
- Pressure Sensors: Pressure transducers and pressure switches are employed to measure fluid or gas pressure in pipelines, tanks, and hydraulic systems, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overpressure conditions.
- Proximity Sensors: Proximity sensors, including inductive, capacitive, and ultrasonic sensors, detect the presence or absence of objects in close proximity, enabling automation and control of material handling and positioning systems.
- Level Sensors: Level sensors, such as float switches, ultrasonic sensors, and capacitance probes, monitor the level of liquids or solids in tanks, silos, and vessels, facilitating inventory management and process control.
Innovations Driving Sensor Technology
- Miniaturization and Integration: Advances in microelectronics have led to the development of miniaturized sensors with integrated signal processing and communication capabilities. These compact sensors offer greater flexibility, reduced installation footprint, and enhanced functionality for a wide range of industrial applications.
- Wireless Connectivity: Wireless sensor networks enable remote monitoring and control of industrial processes, eliminating the need for wired connections and enabling real-time data acquisition from inaccessible or hazardous locations.
- Smart Sensors and IoT Integration: Smart sensors equipped with embedded microcontrollers and communication interfaces enable data processing, analysis, and decision-making at the sensor level. When integrated with IoT platforms, these sensors facilitate predictive maintenance, asset tracking, and optimization of industrial processes.
- Environmental and Energy Monitoring: With growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency, sensors are increasingly used to monitor environmental parameters such as air quality, energy consumption, and emissions. These sensors enable businesses to reduce their environmental footprint and comply with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Industrial sensors are the eyes and ears of modern industry, providing valuable insights into the performance, condition, and efficiency of industrial processes. From temperature and pressure sensors to proximity and level sensors, these devices enable businesses to monitor, control, and optimize operations with precision and confidence. As sensor technology continues to evolve, driven by innovations in miniaturization, connectivity, and smart capabilities, the potential for improving efficiency, safety, and sustainability in industrial settings is limitless. Embracing the power of industrial sensors is not just a strategic advantage—it's a prerequisite for success in the digital age.